The purpose of this document is to provide a detailed overview of “Health Care Data Sharing (POC) using Corda Blockchain” and its parameters and goals. This document can be used by developers, technical architects, and system reviewers for their reference. Through this document, we will cover the healthcare blockchain solutions development. Once we achieve that, we will cover a “Health Care Data Sharing” use case.
Overview
Corda is distributed ledger software for recording and processing shared data such as business contracts. It supports smart contracts, which is an agreement between transacting parties, whose execution is both automatable by computer code, and whose rights and obligations, as expressed in legal prose, are legally enforceable.
- Smart contracts can be written in Java and other JVM languages
- Flow framework to manage communication and negotiation between Hospital
- Peer-to-peer network of nodes.
- “Notary” infrastructure to validate the uniqueness and sequencing of transactions without global broadcast.
Introduction & Background
Why Corda?
Corda is an open-source blockchain platform built for businesses to develop from scratch. Corda blockchain development services enable businesses to transact directly and in strict privacy using smart contracts. As a result, it reduces transaction and record-keeping costs and streamlines business operations.
Key concepts of Corda
Corda is a decentralized database platform having the following features.
- Nodes (Hospital) are arranged in an authenticated peer to peer network. All communication is direct. A gossip protocol is not used.
- In this application, transactions may execute in parallel, on different nodes (Hospital), without either node aware of the others’ transactions.
- Nodes (Hospital) are arranged in an authenticated peer to peer network. All communication is direct. A gossip protocol is not used.
- Currently, this application is having one notary but its network may contain multiple notaries that provide their guarantees using a variety of different algorithms. Corda Blockchain is not tied to any particular consensus algorithm.
- Data is shared on a need-to-know basis. Nodes (Hospital) provide the dependency graph of a transaction they are sending to another node on demand, but there is no global broadcast of all transactions.
- The data model allows for arbitrary object graphs to be stored in the ledger, called states and is the atomic unit of data.
- Nodes(Hospitals) are backed by a relational database and data placed in the ledger can be queried using SQL as well as joined with private tables(Doctor and Patient). States can declare a relational mapping using the Java Persistence Architecture standard (JPA).
Also Read: A Brief Introduction to the Accounts Library in Corda Blockchain
Solving challenges in EHR sharing management
The adoption of Electronic Health Records (EHR) software is a top priority for any health system CIO, yet it’s astronomically expensive and takes significant time and resources to implement.
The biggest challenge faced by the Healthcare industry is the lack of interoperability not just between different organizations’ software platforms but even within a single health provider/system.
For example: If Fortis Delhi wants to share health records of a patient with Apollo Bangalore OR Medanta Delhi, there is no central system to share the information, at the same time ensuring that patient data is secured.
Also Read: Augmenting the Management of EHRs (Electronic Health Records) with Blockchain
Scope
We provide Electronic Health Records (EHR) software, which is very economical and takes less amount of time and resources to implement.
We provide a central system to share the Health-related information, at the same time ensuring that patient’s data is secured.
Blockchain could enable these different systems to talk to one another and provide a complete holistic patient profile without the need for an intermediary to provide any particular validation. Records could be tracked in an audit-able, time-stamped, and immutable ledger so that no one party could ever fraudulently alter them.
Definitions, Acronyms, and Abbreviations
Notary
Notary clusters prevent “double-spends”.
A notary is network service to provide uniqueness consensus attestation for transactions.
Vault
The vault contains data extracted from the ledger that is considered relevant to the node’s owner, stored in a relational model that can be easily queried and worked with.
System Overview with the Following Components
Node
A node’s name must be a valid X.500 distinguished name. In order to be compatible with other implementations (particularly TLS implementations), we constrain the allowed X.500 name attribute types to a subset of the minimum supported set for X.509 certificates (specified in RFC 3280), plus the locality attribute.
RPC
The node’s owner interacts with the node solely via remote procedure calls (RPC). The node’s owner does not have access to the node’s ServiceHub.
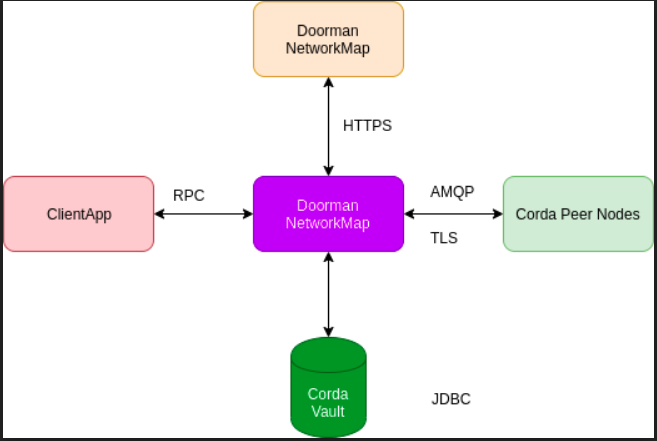
System Architecture
Corda Nodes communicate with each other using an asynchronous protocol, AMQP/TLS. The only HTTP communication is for the initial registration of each Corda Node, and for sharing of the Corda Node address locations by way of the Network Map. Each client application communicates with Corda Nodes using RPC calls. Aso, the Corda Vault is a database that relies on JDBC connection from the Corda Node.
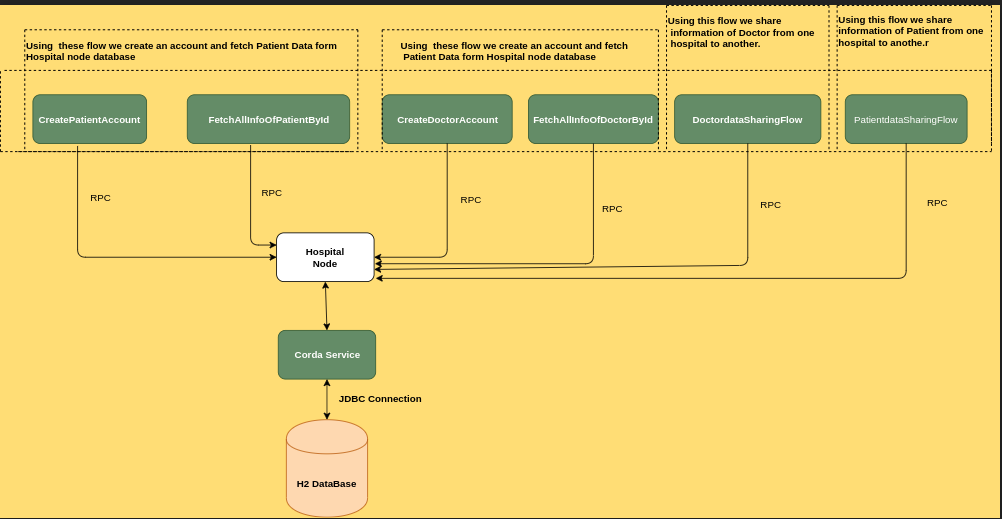
Hospital Data Sharing Flow
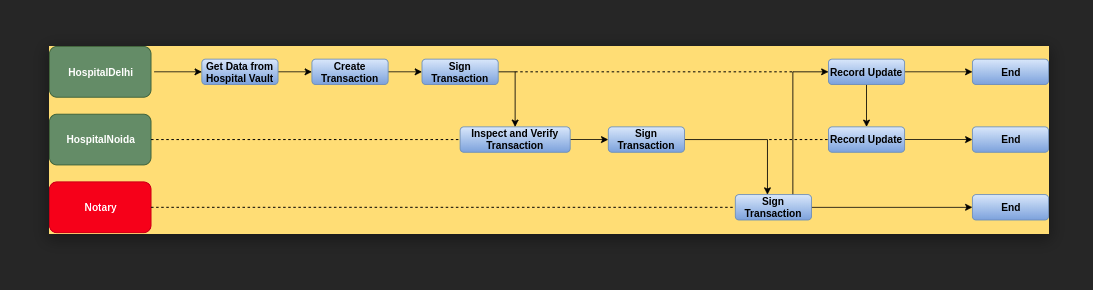
Transaction Steps
Limitations
Currently, we are not able to connect the Spring app with multiple nodes.
Further Improvements
- Role-Based Access in Corda Blockchain
- Add Attachments (For Patients and Doctors)
- Allow multiple Spring Apps to be up at the same time for different Nodes
- Intra Node Communication in Corda Node
References (URLs)
GitLab Repo
https://gitlab.oodleslab.com/oodles/CordaHealthCare.git
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
Average rating 0 / 5. Vote count: 0
No votes so far! Be the first to rate this post.